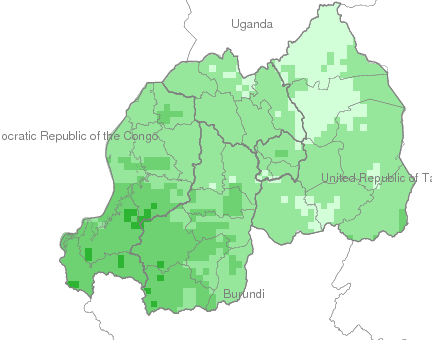
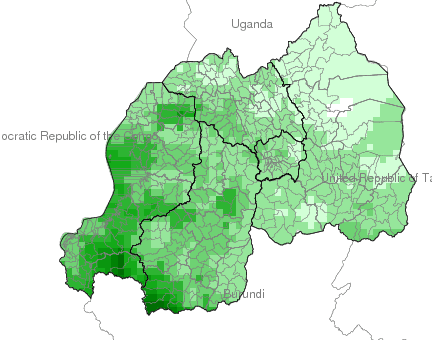
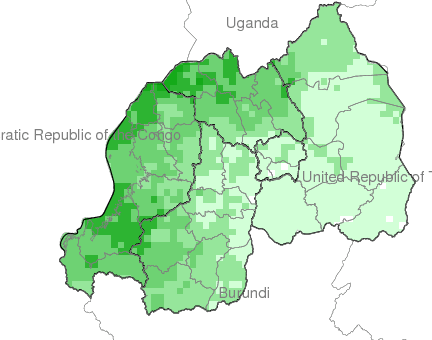
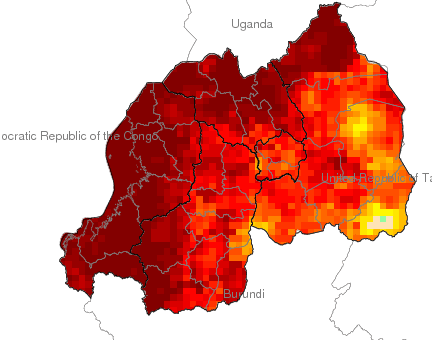
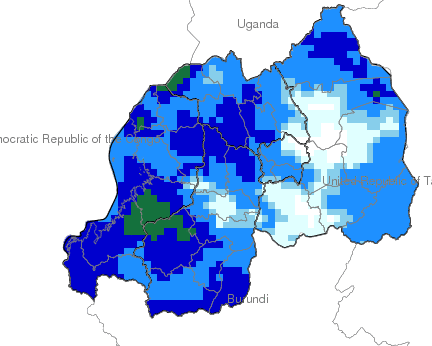
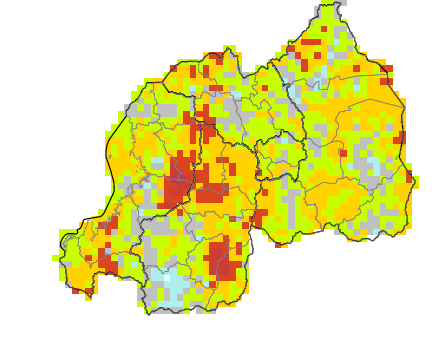
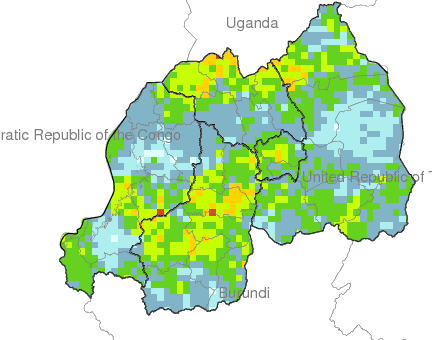
Climate
Climate affects sectors in society in a number of ways. These effects may be direct, as with heat stress, or indirect, as with infectious diseases such as malaria and meningitis.
This facility aims to explore and inform users about the climate-society relationship with an emphasis on the seasonal nature of that relationship, where appropriate.